I have been working on an Office 365 global intranet which will be rolled out to about 55,000 users worldwide. Naturally, one of the core requirements of the solution is that it should be multilingual. In my previous posts on this topic, Modify Site Regional and Language settings with JSOM and JavaScript, we had a look at how to set alternate languages for a site and in Update user language and regional settings with CSOM, we saw how to set the preferred display languages for a user.
This allows a user to see the SharePoint site chrome in their own preferred language. Now in this post, lets have a look at how to have localized custom text so that the user can see custom labels, headings etc. in their preferred language.
Some notes around this:
It is possible to have multi-lingual term sets because each term in a term set has a unique ID and each term can have multiple labels. You can designate a default label for a term in each language available for a term store. A term can then have multiple synonyms in each of these languages, as well as labels and synonyms in other languages.
Users will also see managed terms displayed in their preferred language, regardless of the actual default language of the term store.
If no labels are specified for terms in the language in which a user is viewing a term, then the default label for the term in the default language of the term store will be displayed to users.
https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Work-with-multi-lingual-term-sets-D04098AF-282B-45C3-97CB-59363042C1B3
Lets get started:
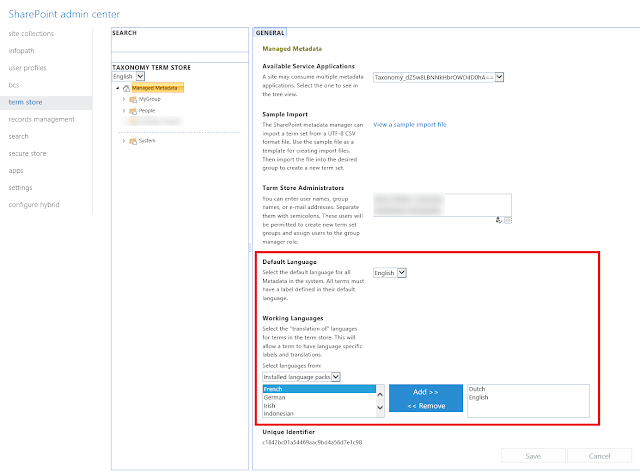
I have set the default language of the Term Store as English and then added Dutch as a Working Language. This means that the term store will be able to support labels for a term in English as well as Dutch.
After adding the working languages, I have created a new Term Group called "My Group".
Under "My Group", I have created a Term Set called "Translations".
Under "Translations", I have created 3 terms: Communications, Marketing and News.
We will use these 3 terms to show the custom multilingual text.
We need to add the default language labels for each term:
After a label has been specified for each term, they will appear in the following way:
When English (default) is selected:
The translation framework will work in the following way:
If I am an English user and I have set my preferred language as English, when the terms for the "Translations" term set will be returned, JSOM will return the English language labels by default.
If I am a Dutch user and I have set my preferred language as Dutch, when the terms for the "Translations" term set will be returned, JSOM will return the Dutch language labels by default.
If I am an Italian user and have set Italian as my preferred language in my user profile, SharePoint will return the English labels for the Translations term set as we have not selected Italian as one of the Working Languages of the Term store, nor have we set any labels in Italian.
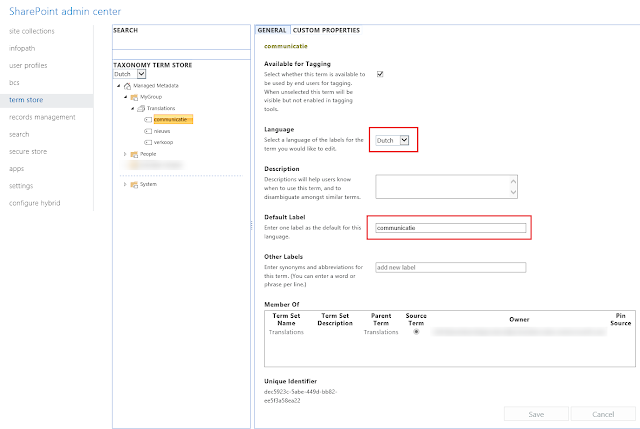
Next, we will add a local custom property for each term to identify it regardless of the language. This will serve as the ID of the term when we fetch it from JSOM:
This is the list of the local custom properties I have created for my terms:
We could use the Term GUID here but I prefer using a custom ID as it is more readable. Also, if someone deletes one of the terms by mistake, it is easy to create a new Term and set the custom ID in the properties. If we were using a GUID, we would have to use code to create a new term with a specific GUID.
Since it is not advisable to make a call to the Term Store on every page load, it is a good idea to cache the labels for a particular user. My recommendation would be to use the browser web storage. Whether you use session storage or local storage depends on the implementation of the solution. MDN has a great article on this https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Storage_API
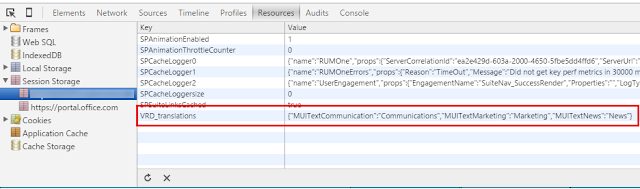
For demo purposes, I am using the sessionStorage and storing the term labels as a JSON object.
When the preferred language of the current user is English:
When the preferred language of the current user is Dutch:
After the framework is correctly setup, all we need to do is call the framework correctly to show the custom text in the language of the current user:
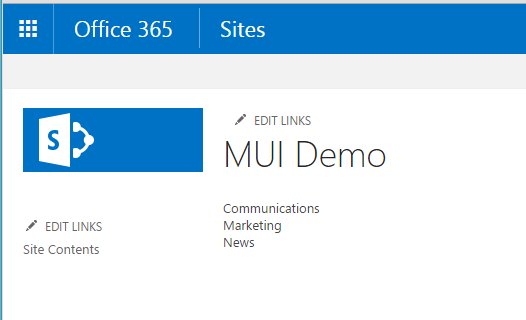
When this code runs, if the preferred language of the current user is English, they will see the English text:
If the preferred language of the current user is Dutch, they will see the custom text in Dutch:
This way, you can utilize the multilingual features of the SharePoint Taxonomy Term Store to show multilingual custom text in your solution.
This allows a user to see the SharePoint site chrome in their own preferred language. Now in this post, lets have a look at how to have localized custom text so that the user can see custom labels, headings etc. in their preferred language.
Some notes around this:
1) This approach is based on the multilingual features of SharePoint Term Sets:
Users will also see managed terms displayed in their preferred language, regardless of the actual default language of the term store.
If no labels are specified for terms in the language in which a user is viewing a term, then the default label for the term in the default language of the term store will be displayed to users.
https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Work-with-multi-lingual-term-sets-D04098AF-282B-45C3-97CB-59363042C1B3
3) Based completely on JSOM, JavaScript and the SharePoint Term Store.
4) This approach is built on top of the MUI features in SharePoint. Which means that the user created content such as list item data, documents etc. will NOT be translated.
5) The SharePoint Online Term Store is treated as a "data source" for custom multilingual text. Each custom text is a term in the "Translations" term set. For each language that you have to support add a new label to the term for that language.
Lets get started:
1) Setup the Term Store to support term labels in multiple languages
I have set the default language of the Term Store as English and then added Dutch as a Working Language. This means that the term store will be able to support labels for a term in English as well as Dutch.
After adding the working languages, I have created a new Term Group called "My Group".
Under "My Group", I have created a Term Set called "Translations".
Under "Translations", I have created 3 terms: Communications, Marketing and News.
We will use these 3 terms to show the custom multilingual text.
We need to add the default language labels for each term:
After a label has been specified for each term, they will appear in the following way:
When English (default) is selected:
When Dutch is selected:
The translation framework will work in the following way:
If I am an English user and I have set my preferred language as English, when the terms for the "Translations" term set will be returned, JSOM will return the English language labels by default.
If I am a Dutch user and I have set my preferred language as Dutch, when the terms for the "Translations" term set will be returned, JSOM will return the Dutch language labels by default.
If I am an Italian user and have set Italian as my preferred language in my user profile, SharePoint will return the English labels for the Translations term set as we have not selected Italian as one of the Working Languages of the Term store, nor have we set any labels in Italian.
2) Add Local Custom Properties to Terms
Next, we will add a local custom property for each term to identify it regardless of the language. This will serve as the ID of the term when we fetch it from JSOM:
This is the list of the local custom properties I have created for my terms:
Term | Local Property Name | Value |
Communications | TranslationID | MUITextCommunication |
Marketing | TranslationID | MUITextMarketing |
News | TranslationID | MUITextNews |
We could use the Term GUID here but I prefer using a custom ID as it is more readable. Also, if someone deletes one of the terms by mistake, it is easy to create a new Term and set the custom ID in the properties. If we were using a GUID, we would have to use code to create a new term with a specific GUID.
3) The Translation framework
After the Term Store is correctly setup, all we need to do is get the terms from the "Translations" term using the JavaScript Client Object Model (JSOM) and display them in the UI:
- Query the term store to get the terms from the "Translations" term set.
- SharePoint will return the term labels in the current user's preferred language if:
- The alternate language is enabled on the current site
- The current user has set the language as a preferred language in their user profile
- The term store supports the language as a "Working Language" as shown in step 1
- A default label is defined for the terms in that language.
- If any one of these conditions is not fulfilled, then the English labels for the terms will be fetched as it is the default language of the Term Store.
- The term labels will be stored in the cache.
4) Performance/Caching
Since it is not advisable to make a call to the Term Store on every page load, it is a good idea to cache the labels for a particular user. My recommendation would be to use the browser web storage. Whether you use session storage or local storage depends on the implementation of the solution. MDN has a great article on this https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Storage_API
For demo purposes, I am using the sessionStorage and storing the term labels as a JSON object.
When the preferred language of the current user is English:
When the preferred language of the current user is Dutch:
5) Using the framework to show localized text
After the framework is correctly setup, all we need to do is call the framework correctly to show the custom text in the language of the current user:
When this code runs, if the preferred language of the current user is English, they will see the English text:
If the preferred language of the current user is Dutch, they will see the custom text in Dutch:
This way, you can utilize the multilingual features of the SharePoint Taxonomy Term Store to show multilingual custom text in your solution.